A popular (but misleading) term for a trading system through which countries may buy or sell units of greenhousegas emissions in an effort to meet their national limits on emissions, either under the Kyoto Protocol or under other agreements, such as that among member states of the European UnionThe gas traps heat and how long it stays in the atmosphere To compare the impact of each GHG, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) developed the concept of the Global Warming Potential (GWP), which relates each gas's ability to trap heat in the atmosphere to the reference gas, CO 2 (IPCC 14) By definition, CO 2 has a If countries continue on their current paths, with greenhouse gas emissions likely to bring 34 C of warming (5472 F) by 2100, the planet

Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gas emissions definition ipcc
Greenhouse gas emissions definition ipcc-And renewable energy technologies, the majority of GHG emissions occur upstream of operation LCA of Energy Systems Life Cycle Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Electricity Generation As clean energy increasingly becomes part of the national dialogue, lenders, utilities, and lawmakers need the most comprehensive and accurate information on GHG 06 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 06) 15 The People's Republic of




From Farm To Fork Fighting Climate Change Is Actually Possible Zero Waste Europe
Within IPCC the National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Program develops methodologies to estimate emissions of greenhouse gases This has been undertaken since 1991 by the IPCC WGI in close collaboration with the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development and the International Energy AgencyA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface wouldIn order to ensure precision and reliability, national GHG inventories are required to fulfil certain criteria, as laid out in the IPCC Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management in National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (hereinafter referred to as the IPCC good practice guidance)6 Thus, the inventories must be
The term "anthropogenic", in the context of greenhouse gas inventories, refers to greenhouse gas emissions and removals that are a direct result of human activities or are the result of natural processes that have been affected by human activities Atmosphere The gaseous envelope surrounding the EarthLarger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere4 EEA, Determination of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Limit for (Dec 28, 10) 5 Decision of the 21st Conference of Parties of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to adopt the Paris Agreement (Jan 29, 16), para 21 6 IPCC, Special Report on Global Warming of 15°C (Oct 18), Chap 3 ("Impacts of 15°C of Global
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from postconsumer waste and wastewater are a small contributor (about 3%) to total global anthropogenic GHG emissions Emissions for 0405 totalled 14 Gt CO2eq year(1) relative to total emissions from all sectors of 49 Gt CO2eq year(1) including carbon dioxi Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeEquivalent emissions in this report are—if not stated otherwise—aggregated using global warming potentials (GWPs) over a 100year time horizon, often derived from the IPCC Second Assessment Report (IPCC, 1995a) A discussion about different GHG



Temperatures Climate Action Tracker
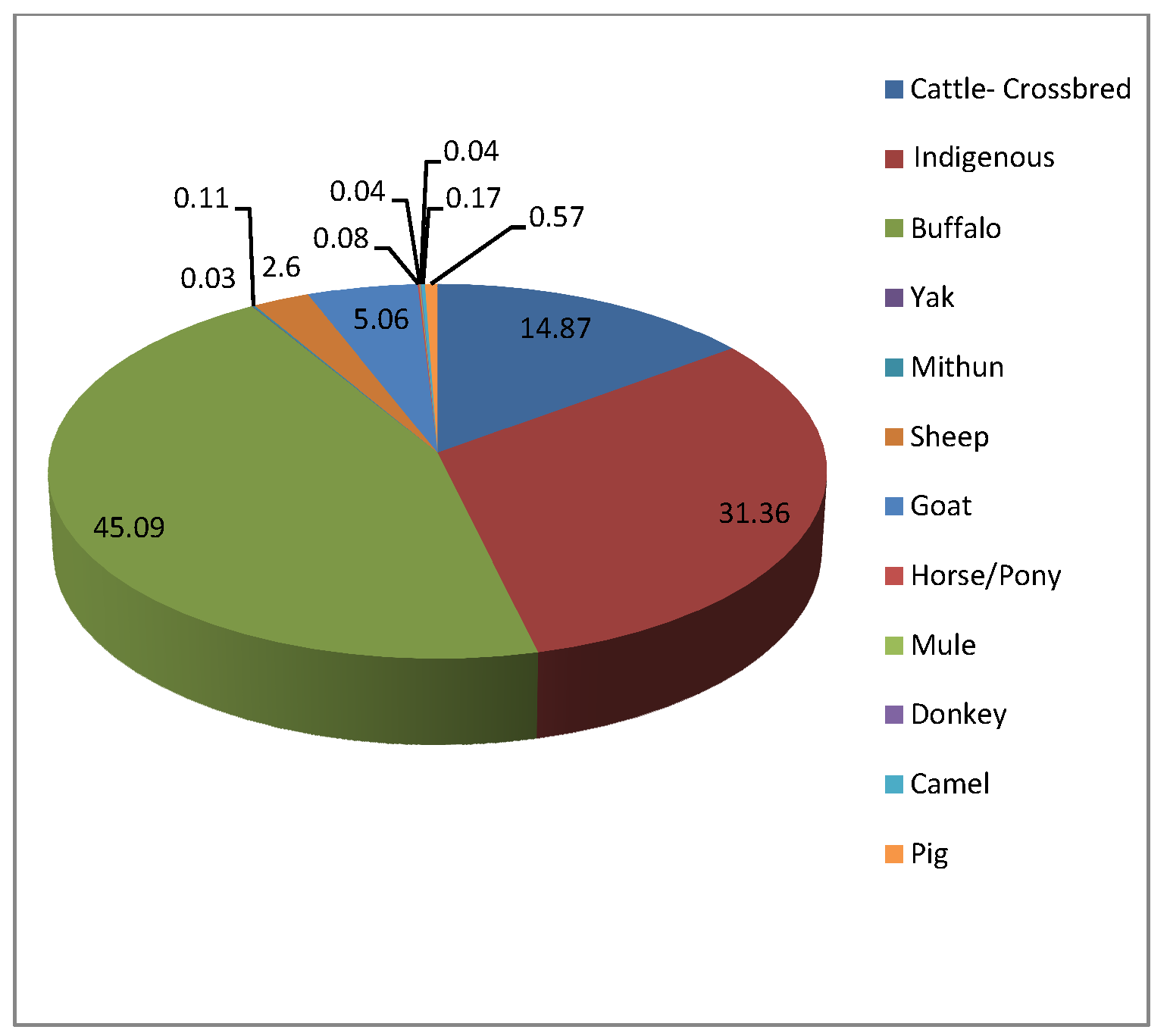



Livestock As Sources Of Greenhouse Gases And Its Significance To Climate Change Intechopen
The EPA's Inventory of US Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks (Inventory) complies with international GHG reporting standards under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) UNFCCC guidelines now require the use of the GWP values for the IPCC's Fourth Assessment Report (AR4), published in 07This chapter frames the context, knowledgebase and assessment approaches used to understand the impacts of 15°C global warming above preindustrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, building on the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report (AR5), in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development and efforts to eradicate povertyEmissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs), precursors of GHGs and aerosols caused by human activities These activities include the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, land use and landuse changes (LULUC), livestock production, fertilisation, waste management and industrial processes See also Anthropogenic and Anthropogenic removals




From Farm To Fork Fighting Climate Change Is Actually Possible Zero Waste Europe




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a group of substances that contribute to global warming They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), perfluorocarbons (PFCs) hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and many other compounds listed by the IPCC* The 100year GlobalIn discussions on climate change, we tend to focus on carbon dioxide (CO 2) – the most dominant greenhouse gas produced by the burning of fossil fuels, industrial production, and land use changeWe cover CO 2 – global emissions, annual, cumulative, per capita, and consumptionbased emissions – in great detail in our CO 2 emissions page But CO 2 is not the only greenhouse gasThe IPCC Special Report on Aviation demonstrates that the total impact of a sector is not represented by (nor scalable to) the direct emissions of primary greenhouse gases alone, but needs to consider a wide range of atmospheric changes
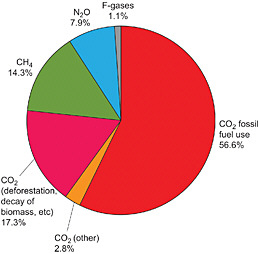



1 Introduction Verifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions Methods To Support International Climate Agreements The National Academies Press



Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide And Several Shades Of Green Orkas
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Draft Environmental Impact Report 481 IPCC defines the GWP of various GHG emissions on a normalized scale that recasts all GHG emissions which compares the gas in question to that of the same mass of CO 2 (by definition, CO 2 has a GWP of 1) The global warming potential of a GHG is a The IPCC's projections for global average sea level rise in metres with higherimpact pathways and the level of greenhouse gas emissions IPCC Sixth Assessment Report What's more, the more the world limits its greenhouse gas emissions, the lower the chance of triggering instabilities in the polar ice sheets that are challenging to model but The emissions sources covered include travel to and from an event, emissions from hotel stays by attendees, and emissions from the event or conference venue Retailers can also use the ENERGY STAR Scope 3 Use of Sold Products Analysis Tool V10 (XLSM) to benchmark and project corporate Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions associated with the use
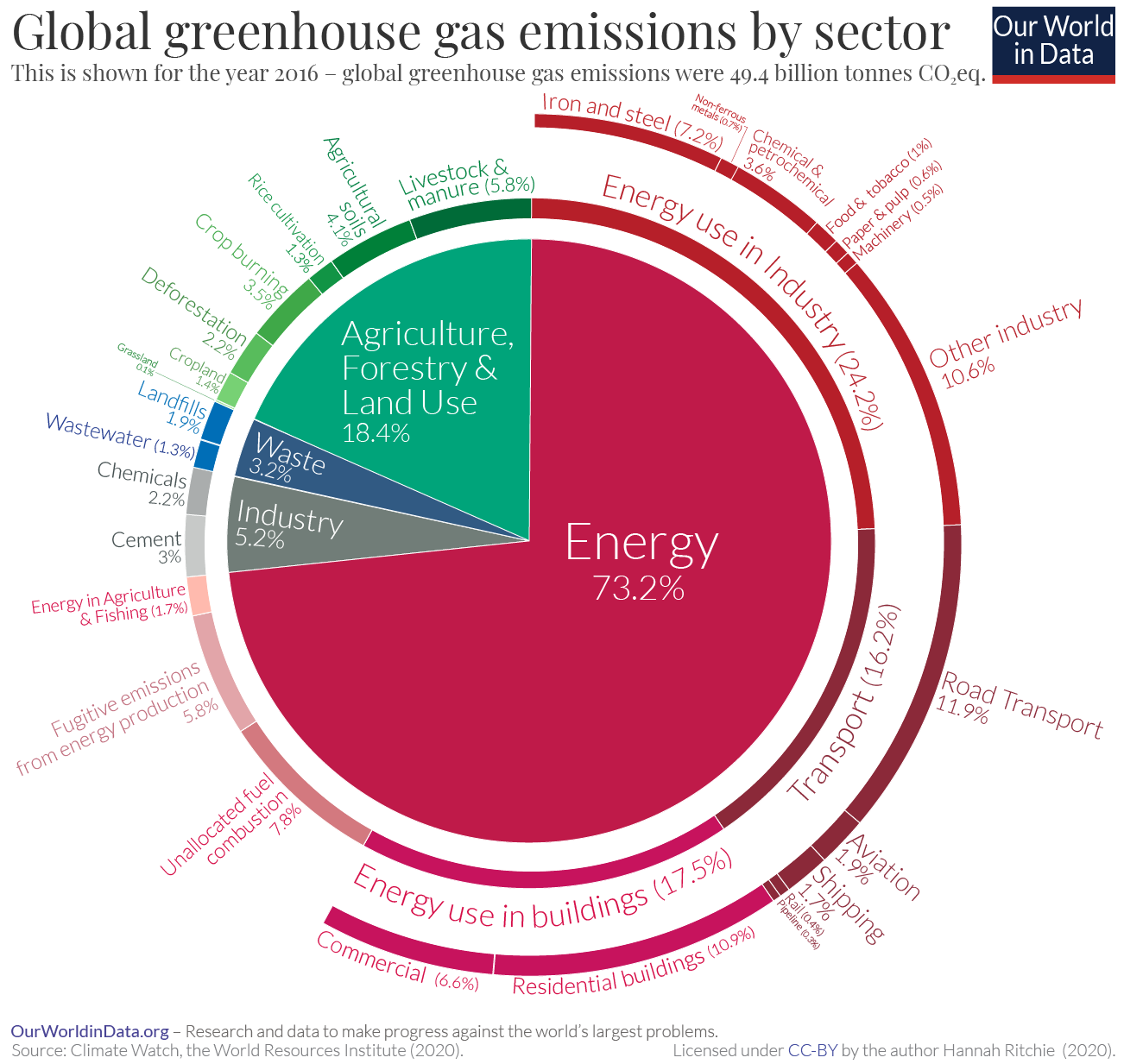



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data




Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions From International Air Travel Of A Country S Residents Methodological Development And Application For Sweden Sciencedirect
Greenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate changeMost is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and RussiaAll greenhouse gas data presented here reflect the information reported to EPA as of The reported emissions exclude biogenic CO 2GHG data displayed are in units of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO 2 e) and reflect the global warming potential (GWP) values from Table A1, which is generally based on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)'s FourthA carbon credit is a permit that allows the company that holds it to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases One credit permits the emission of a mass equal to one ton



Statswiki Unece Org Download Attachments Ccci 11 2509 Pdf Version 1 Modificationdate Api V2
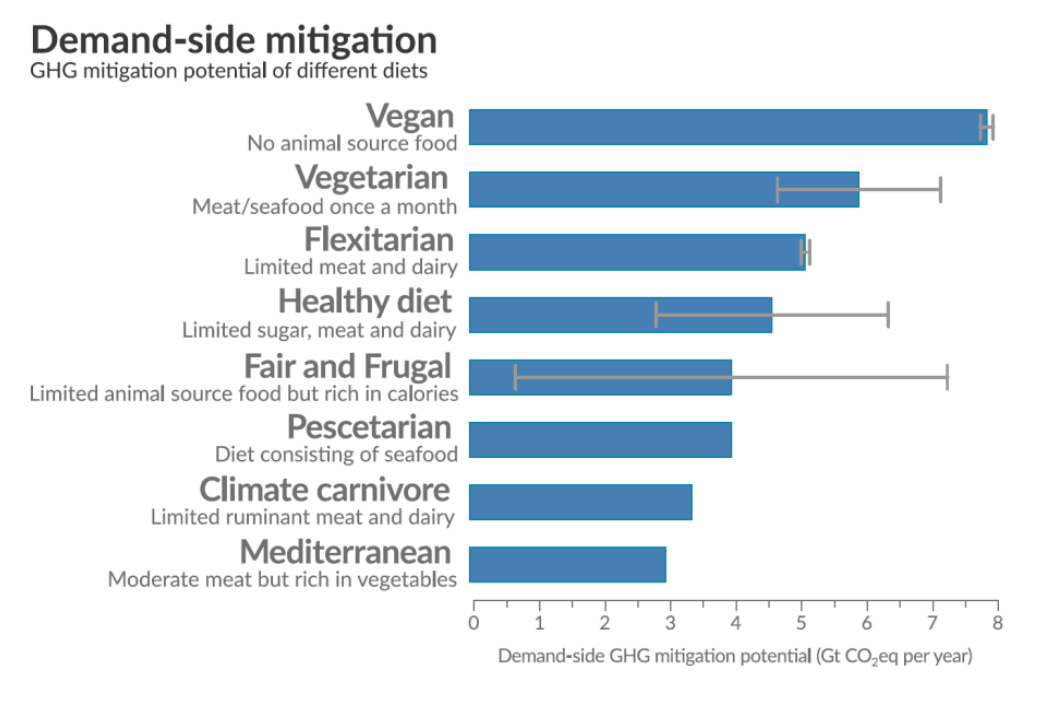



Ipcc S Land Report Showed We Re Entering An Era Of Damage Control
0019 GHG Inventory (21 Edition) The California Greenhouse Gas Emissions for 00 to 19, Trends of Emissions and Other Indicators, summarizes and highlights the major annual changes and notable longerterm trends of each year's GHG inventory It provides easytoread graphs and explanations to illuminate California's progress in its commitment to reduce climatechanging emissionsThe European Environment Agency (EEA) compiles an annual greenhouse gas inventory report on behalf of the EU Estimates of greenhouse gas emissions are produced for a number of sources which are delineated in sectors primarily according to the technological source of emissions, as devised by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC UN Climate Change News, – The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released on Monday an update to its methodology used by governments to estimate their greenhouse gas emissions and removals



Two Decades From Disaster The Ipcc S Global Warming Of 1 5 C Historicalclimatology Com
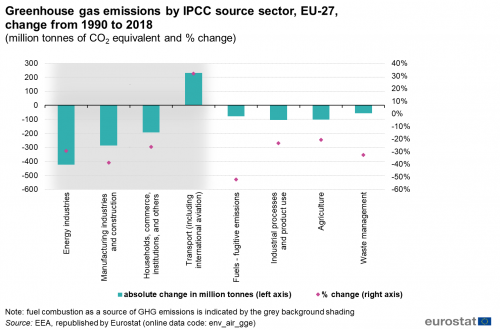



Climate Change Driving Forces Statistics Explained
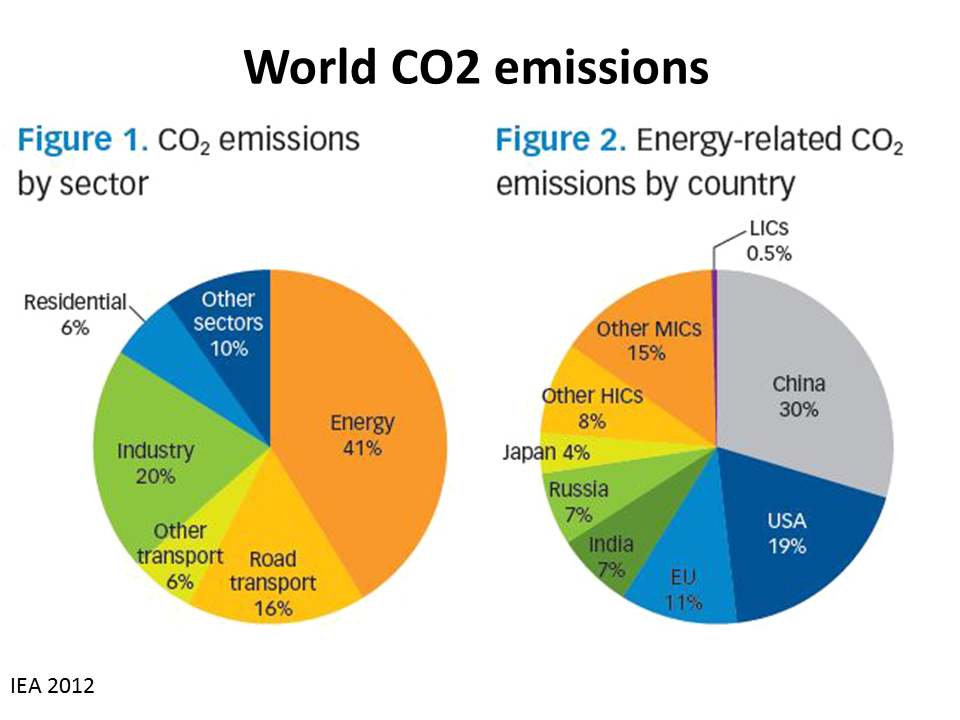
So reducing greenhouse gas emissions is hugely important, but we can't stop there The end goal is to balance the scales again, and restore the global climate to preclimate change levels To get there, we need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to zero AND then get cracking on repairing past harm by drawing down past emissionsIndustry (21% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) Greenhouse gas emissions from industry primarily involve fossil fuels burned on site at facilities IPCC Sixth Assessment Report Humans produce large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through fossil fuel burning, agriculture, deforestation and decomposing waste




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Carbon Budgets Where Are We Now Carbon Tracker Initiative
A sizable portion of recent studies on future climate impacts have focused on a future warming scenario called "RCP85" This highemissions scenario is frequently referred to as "business as usual", suggesting that is a likely outcome if society does not make concerted efforts to cut greenhouse gas emissions IPCC Methodologies Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere such as water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide that can absorb infrared radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere This greenhouse effect means that emissions of greenhouse gases due to human activity cause global warming If countries continue on their current paths, with greenhouse gas emissions likely to bring 34 C of warming (5472 F) by 2100, the planet



Carbon Emissions Energy Economics Home




Meeting Report Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas
Our history is being written For three decades the IPCC has been warning of the dangers of climate change, yet the world has not taken strong enough action to halt it This report is clear that unless there are immediate, rapid and largescale reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, limiting warming to close to 15C or even 2C will be beyond Electricity and Heat Production (25% of 10 global greenhouse gas emissions) The burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat is the largest single source of global greenhouse gas emissions;Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases




Science Based Targets Decoding Sustainability



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
1 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC 06) 06 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme, Eggleston HS, Buendia L, Miwa K, Ngara T andMeasurement of lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions involves calculating the globalwarming potential of energy sources through lifecycle assessmentThese are usually sources of only electrical energy but sometimes sources of heat are evaluated The findings are presented in units of global warming potential per unit of electrical energy generated by that sourceAt the same time, keeping global warming to well below 2ºC can be achieved only by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from all sectors including land
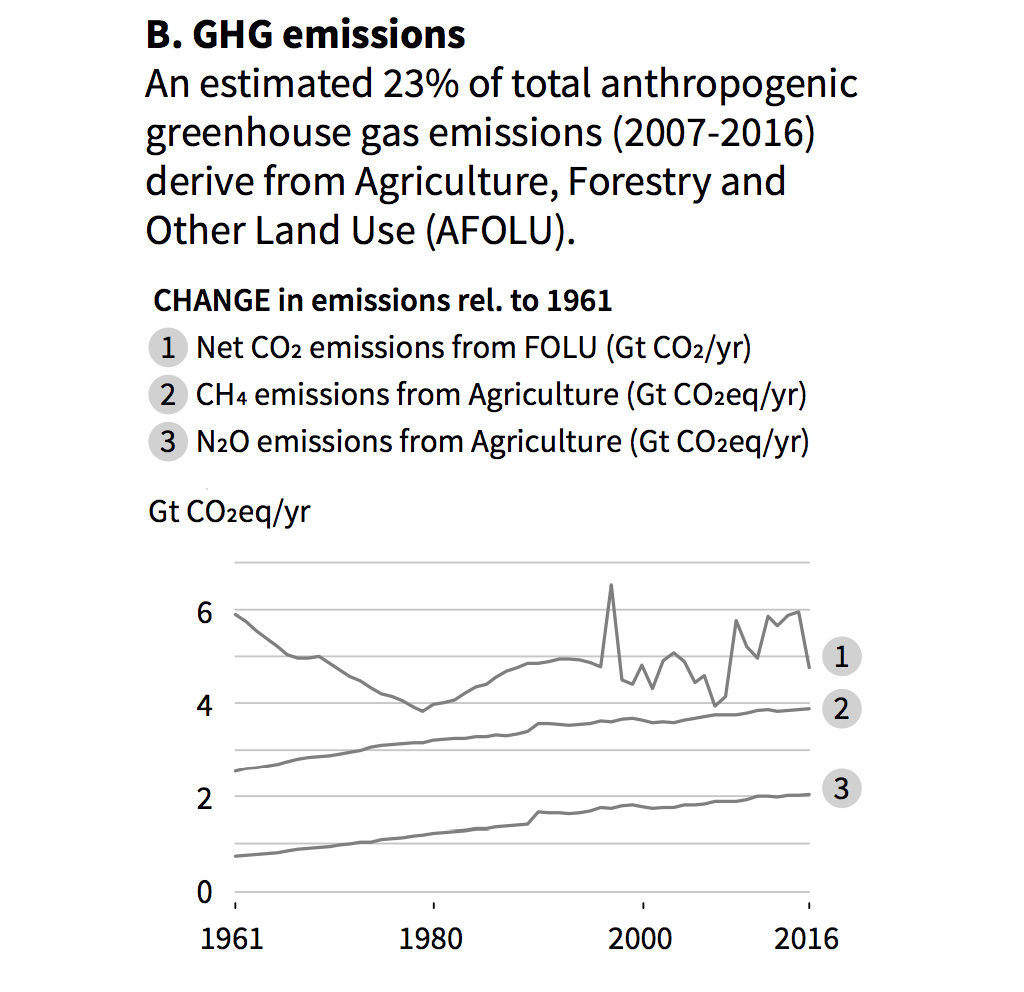



What The New Ipcc Report Says About Climate Change And Land Climate Capitalism




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was established by the World Meteorological 37 Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change San Francisco VA Medical Center Long Range Development Plan 373 Final EIS Greenhouse Gases and Global Emission Sources has a GWP of 1 by definition) As such, a high37 Greenhouse Gas Emissions LA River Master Plan Program EIR 372 February 21 ICF 54 Increases in fossil fuel combustion and deforestation have exponentially increased concentrations of GHGs in the atmosphere since the Industrial Greenhouse Gases at EPA Before there were federal requirements to do so, EPA had developed a greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions inventory and established reduction targets to decrease its GHG footprint There are three types of GHG emissions EPA tracks and works to reduce View a larger version of this image




Commitment




Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
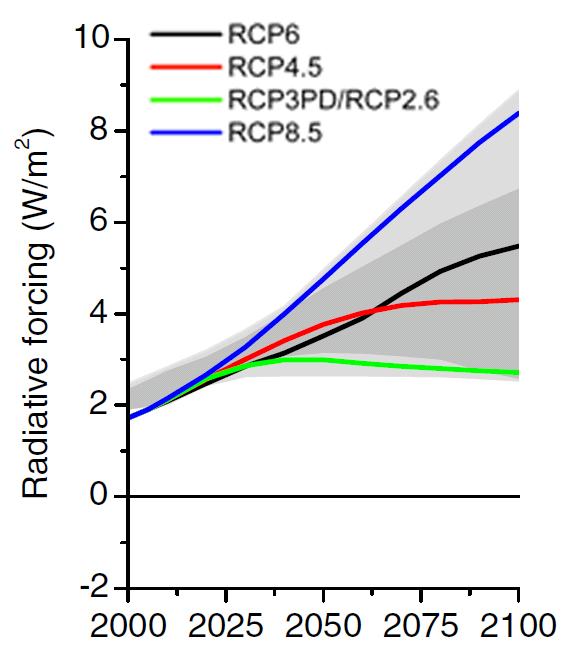
The Emission Factor Database (EFDB) is a project supported by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme (NGGIP), which is managed by the IPCC Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (TFI) EFDB is intended to be a recognized library, where users can find emission factors and other parameters with background documentation or technicalA Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) is a greenhouse gas concentration (not emissions) trajectory adopted by the IPCC Four pathways were used for climate modeling and research for the IPCC fifth Assessment Report (AR5) in 14 The pathways describe different climate futures, all of which are considered possible depending on the volume of greenhouse gases (GHG) emitted in
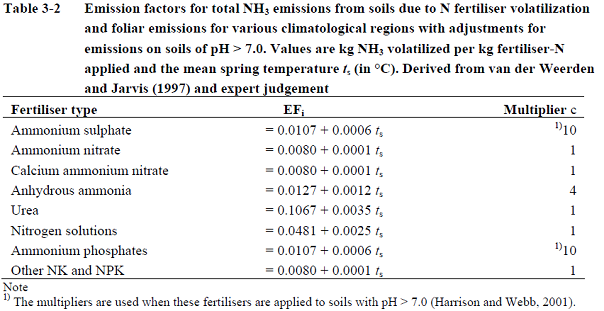



Faqs Ipcc Tfi




Glossary Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas Inventories
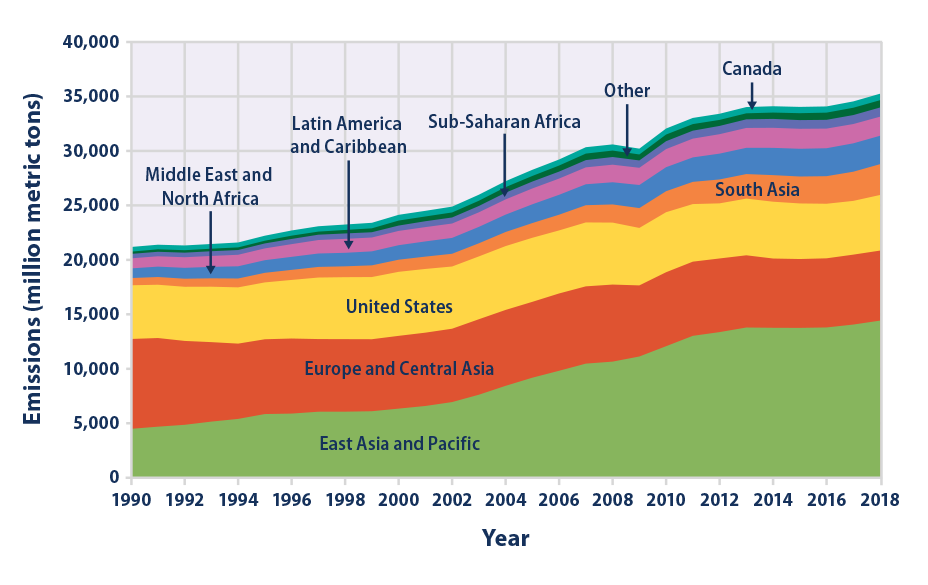



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Embodied Ghg Emissions Of Buildings The Hidden Challenge For Effective Climate Change Mitigation Sciencedirect



Http Www Fao Org 3 I4260e I4260e Pdf




The Greenhouse Gases Airclim




Global Warming And Climate Change The Science World Nuclear Association
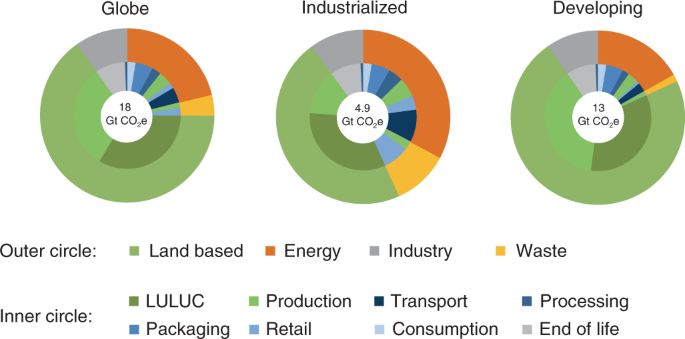



Food Systems Are Responsible For A Third Of Global Anthropogenic Ghg Emissions Nature Food



Socio Economic Data And Scenarios



Frontiers Agriculture S Contribution To Climate Change And Role In Mitigation Is Distinct From Predominantly Fossil Co2 Emitting Sectors Sustainable Food Systems



Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide



Forests And Climate Change
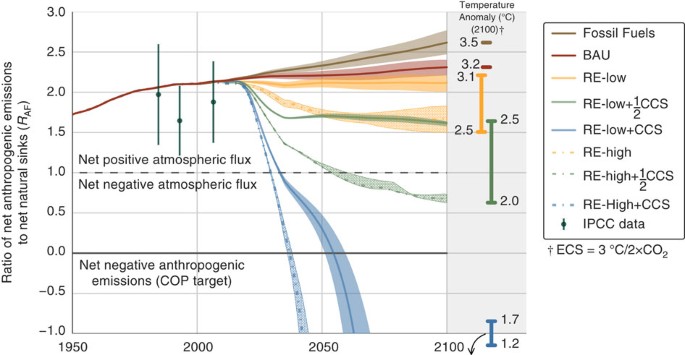



Pathways For Balancing Co 2 Emissions And Sinks Nature Communications




The Ipcc S Climate Change Report Negative Emissions And Business As Usual Redd Monitor




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
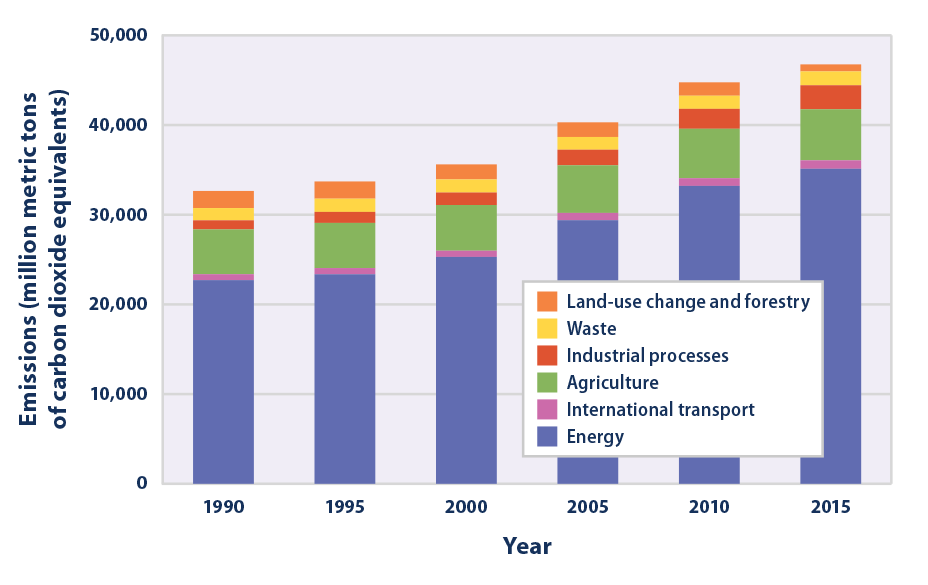



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Climate Change And Land Ipcc S Report Drishti Ias
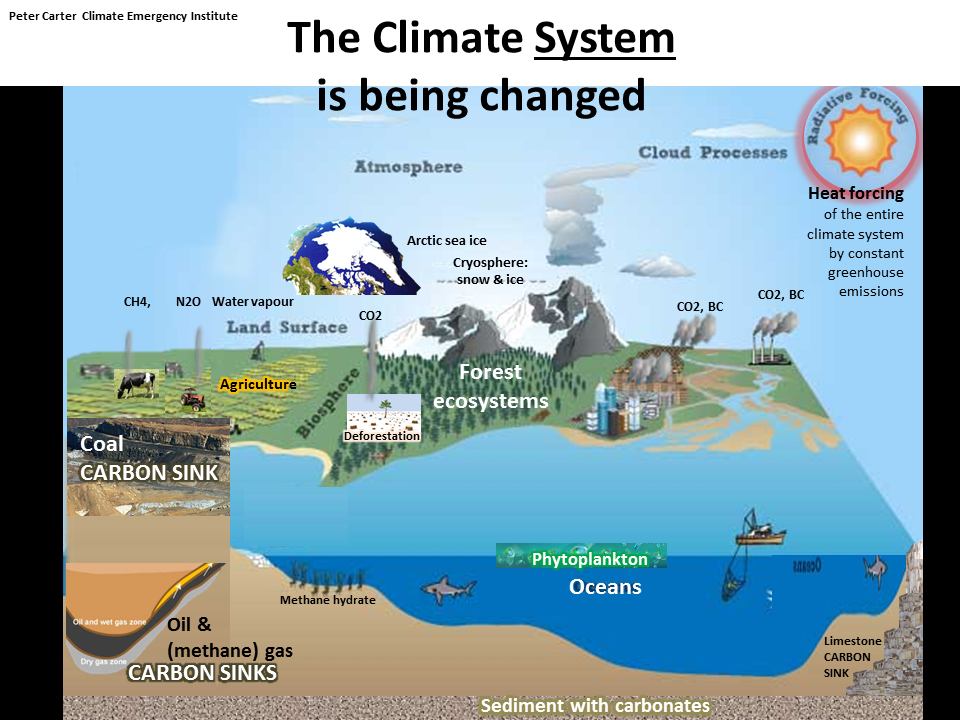



Climate Science
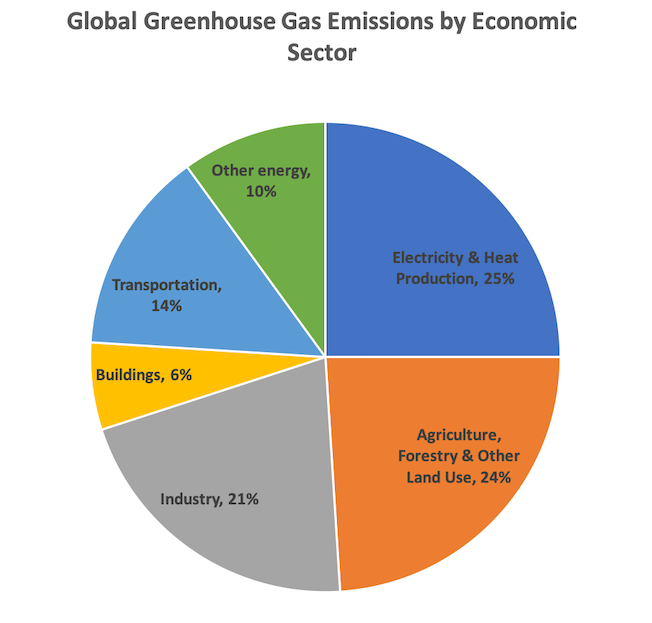



Climate Challenge Cut The Gray Carbon Wedge Of Industrial Emissions Aceee
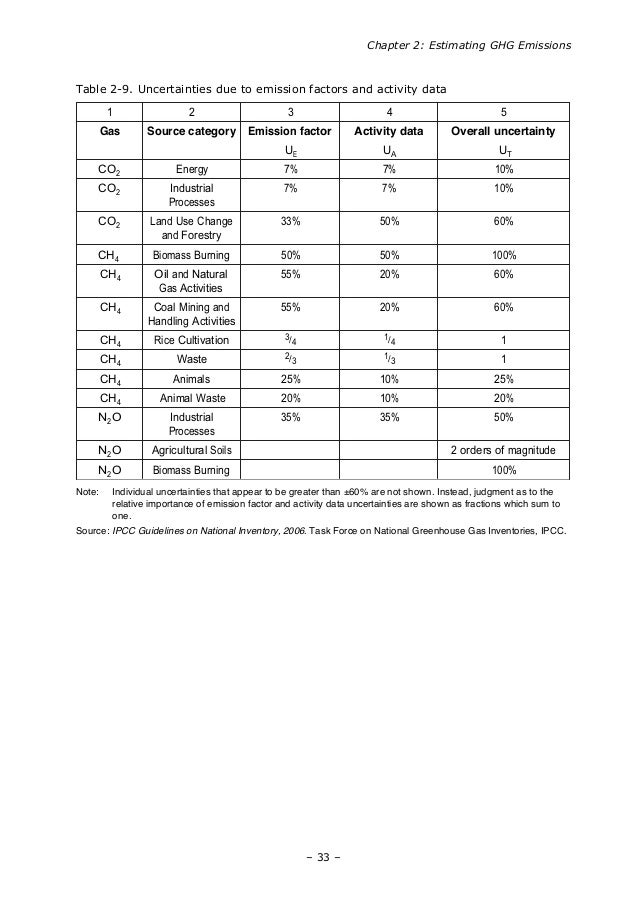



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Estimation And Reduction




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
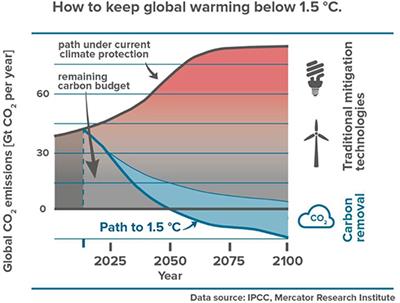



Frontiers The Role Of Direct Air Capture In Mitigation Of Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Climate




Rcp8 5 Tracks Cumulative Co2 Emissions Pnas




Topic 1 Observed Changes And Their Causes Ipcc



Sectoral Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Ipcc Sector European Environment Agency
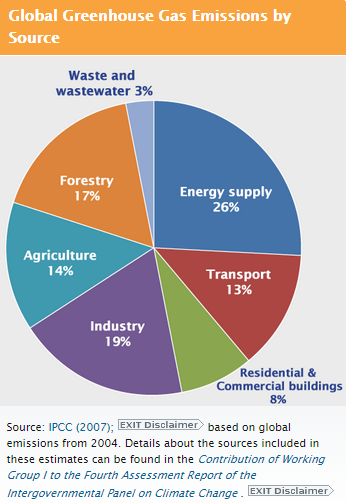



Is A Net Zero World Even Possible
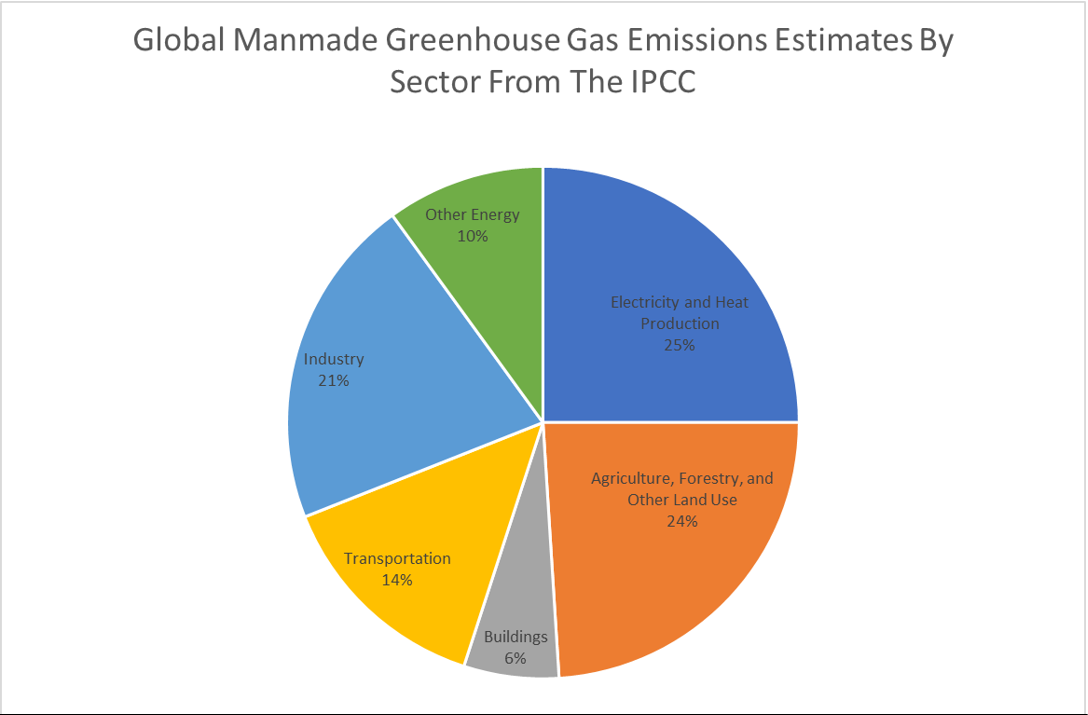



How Much Does Animal Agriculture And Eating Meat Contribute To Global Warming




Major Greenhouse Gas Reductions Needed By 50 Ipcc Climate Central




Ipcc Everything And The Carbon Sink



Climateactiontransparency Org Wp Content Uploads 10 Non State And Subnational Action Guide Ch4 Pdf




Net Phase Out Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Newclimate Institute



The Science Of Carbon Footprint Assessment




Summary For Policymakers Ipcc
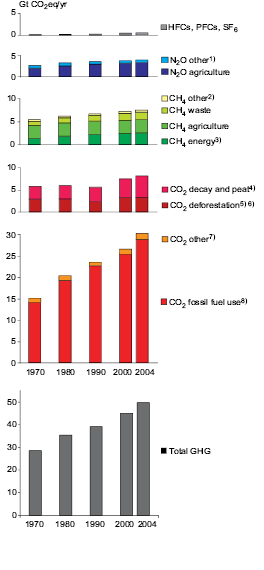



B Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends Ar4 Wgiii Summary For Policymakers



Ipcc Confirms That Global Temperature Change Can Still Be Limited To Less Than 2 C But Current Trends Make It Much More Difficult Controlling Climate Change




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Http Www Thegef Org Sites Default Files Council Meeting Documents En Gef C 48 Inf 09 Guideline On Ghg Accounting And Reporting For Gef Projects 5 Pdf




Source Ipcc 07 Ghg Emissions Scenarios Global Ghg Emissions In Download Scientific Diagram



Defining Dangerous Climate Change
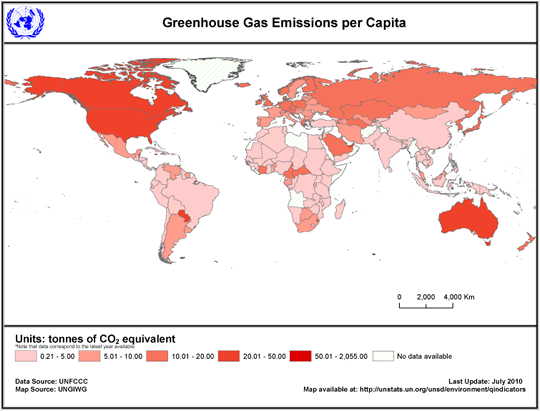



United Nations Statistics Division Environment Statistics



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Climate Change Scenario Wikipedia




Measurement Reporting Verification And Certification Of Methane Emissions From Fossil Fuel Production And Natural Gas Value Chains G Insights
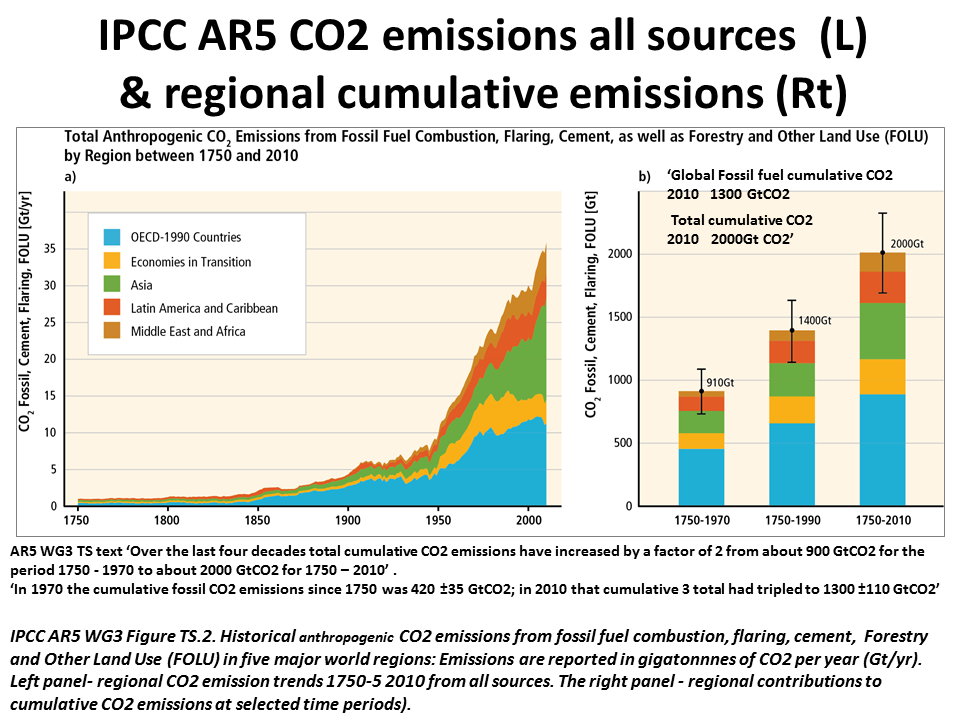



Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
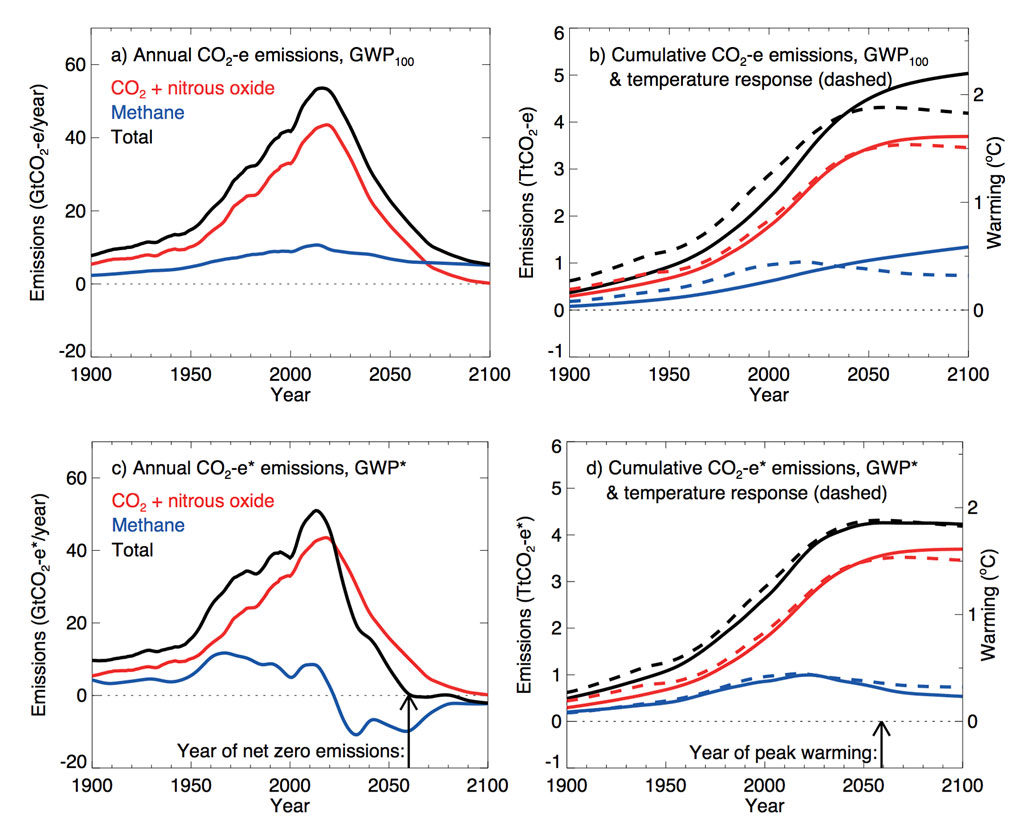



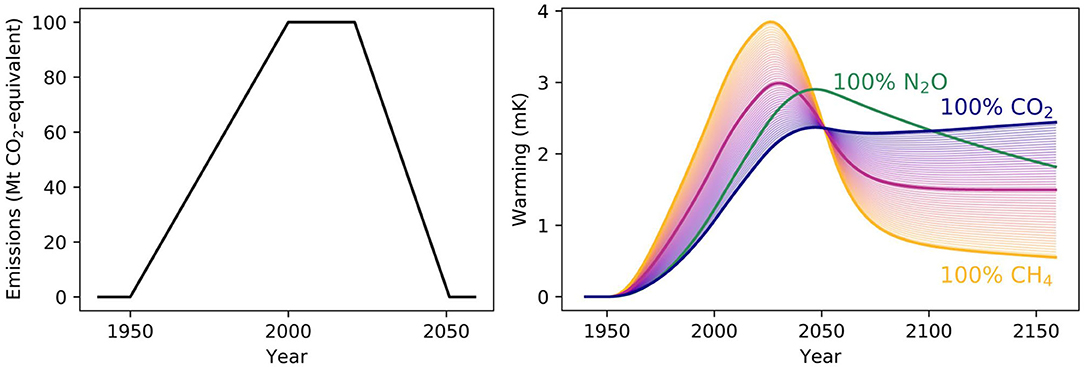
Guest Post A New Way To Assess Global Warming Potential Of Short Lived Pollutants




Centred On Science How The Ipcc Can Guide Mitigation Action Climate Analytics



Www Mdpi Com 1996 1073 13 4 800 Pdf




Measurement Reporting Verification And Certification Of Methane Emissions From Fossil Fuel Production And Natural Gas Value Chains G Insights



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau




Remarkable Changes To Carbon Emission Budgets In The Ipcc Special Report On Global Warming Of 1 5c Climate Etc
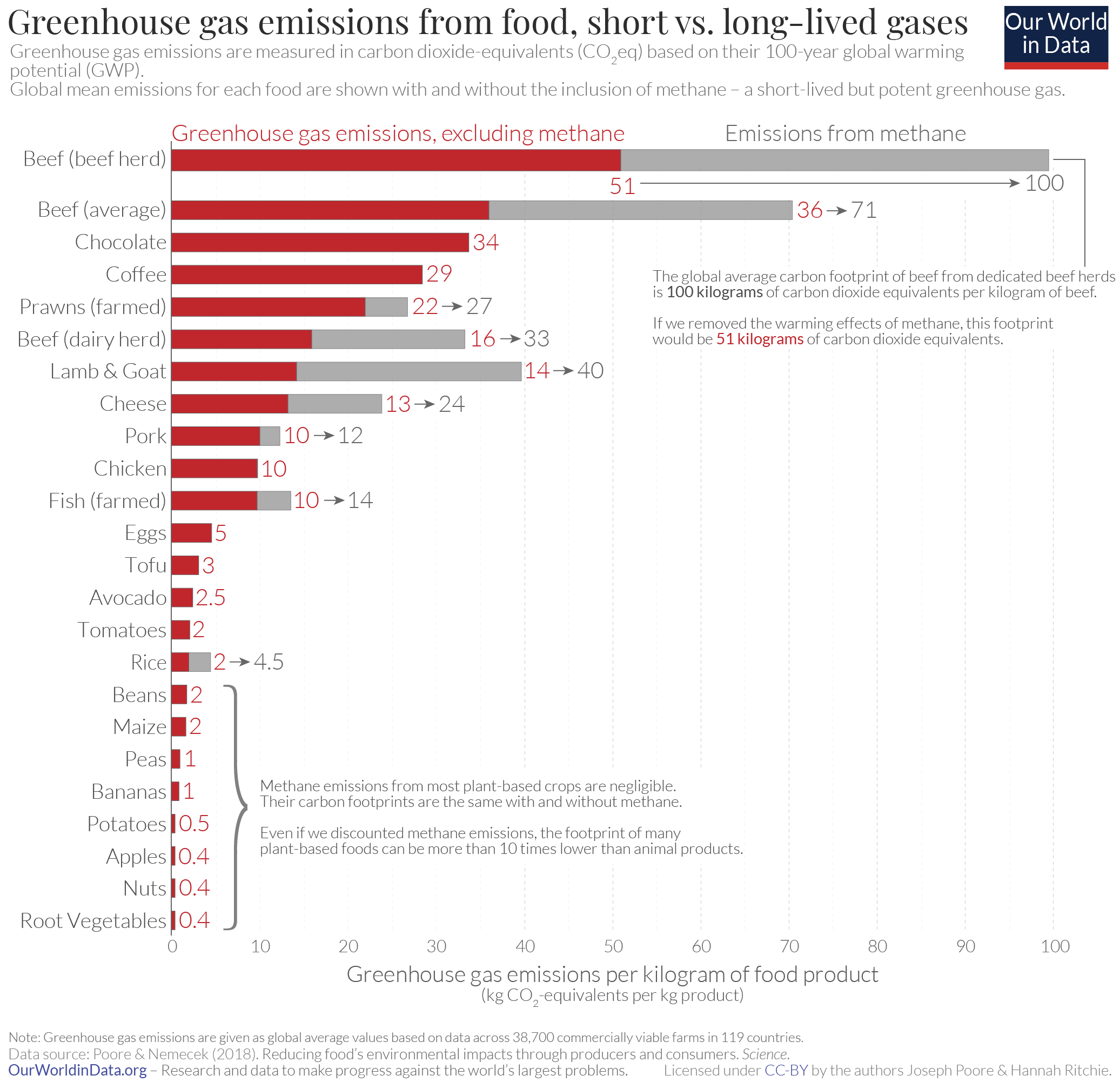



The Carbon Footprint Of Foods Are Differences Explained By The Impacts Of Methane Our World In Data



Sea Level Rise Coastal Wiki
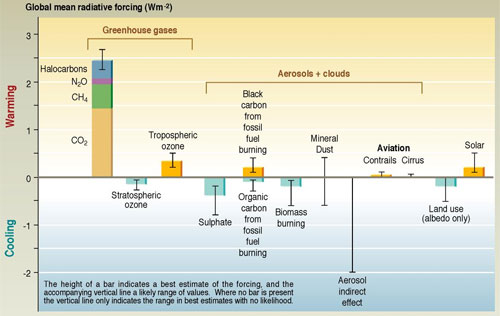



What Is Methane S Contribution To Global Warming




Iso 2 19 En Greenhouse Gases Part 2 Specification With Guidance At The Project Level For Quantification Monitoring And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions Or Removal Enhancements




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions A By Type Of Gases B By Type Of Download Scientific Diagram




A New Methodology For Organic Soils In National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Data Synthesis Derivation And Application Sciencedirect
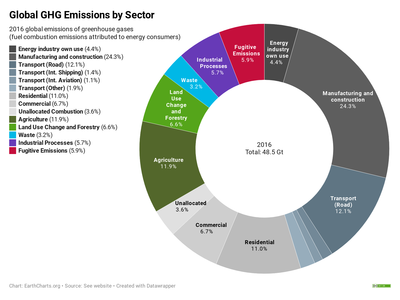



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia



1




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Net Phase Out Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Newclimate Institute



1




Fifth Assessment Report Synthesis Report By Ipcc Issuu
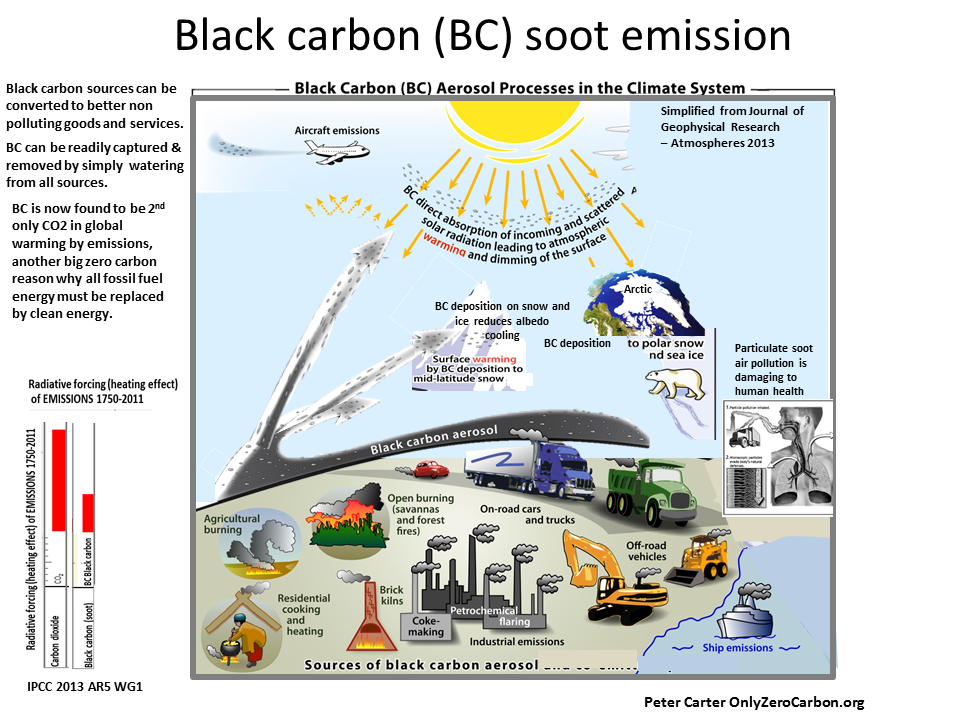



Climate Science




The Ipcc Special Report On Emission Scenarios Sres Produced Four Download Scientific Diagram
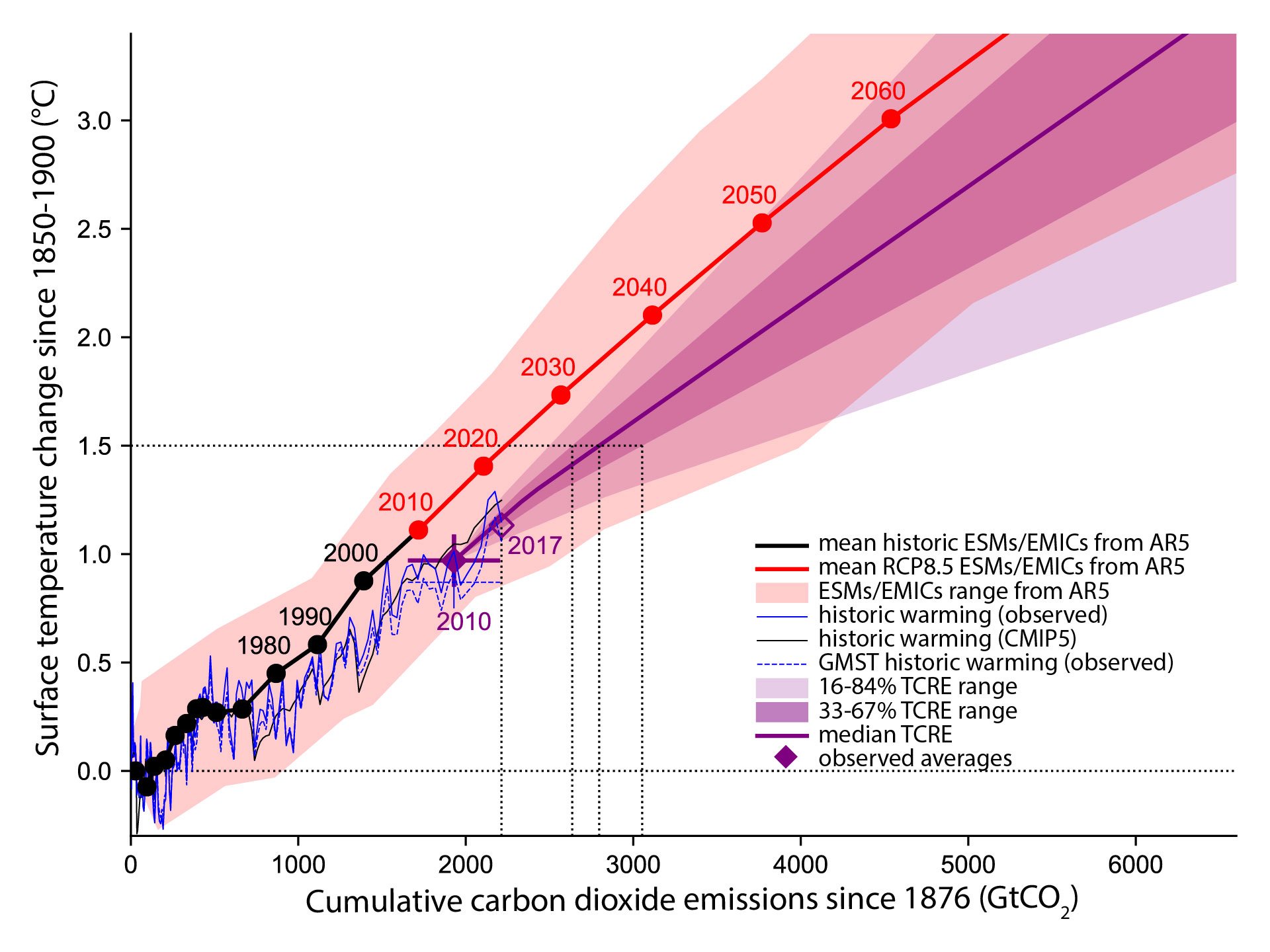



Chapter 2 Global Warming Of 1 5 ºc




Attributing Long Term Sea Level Rise To Paris Agreement Emission Pledges Pnas
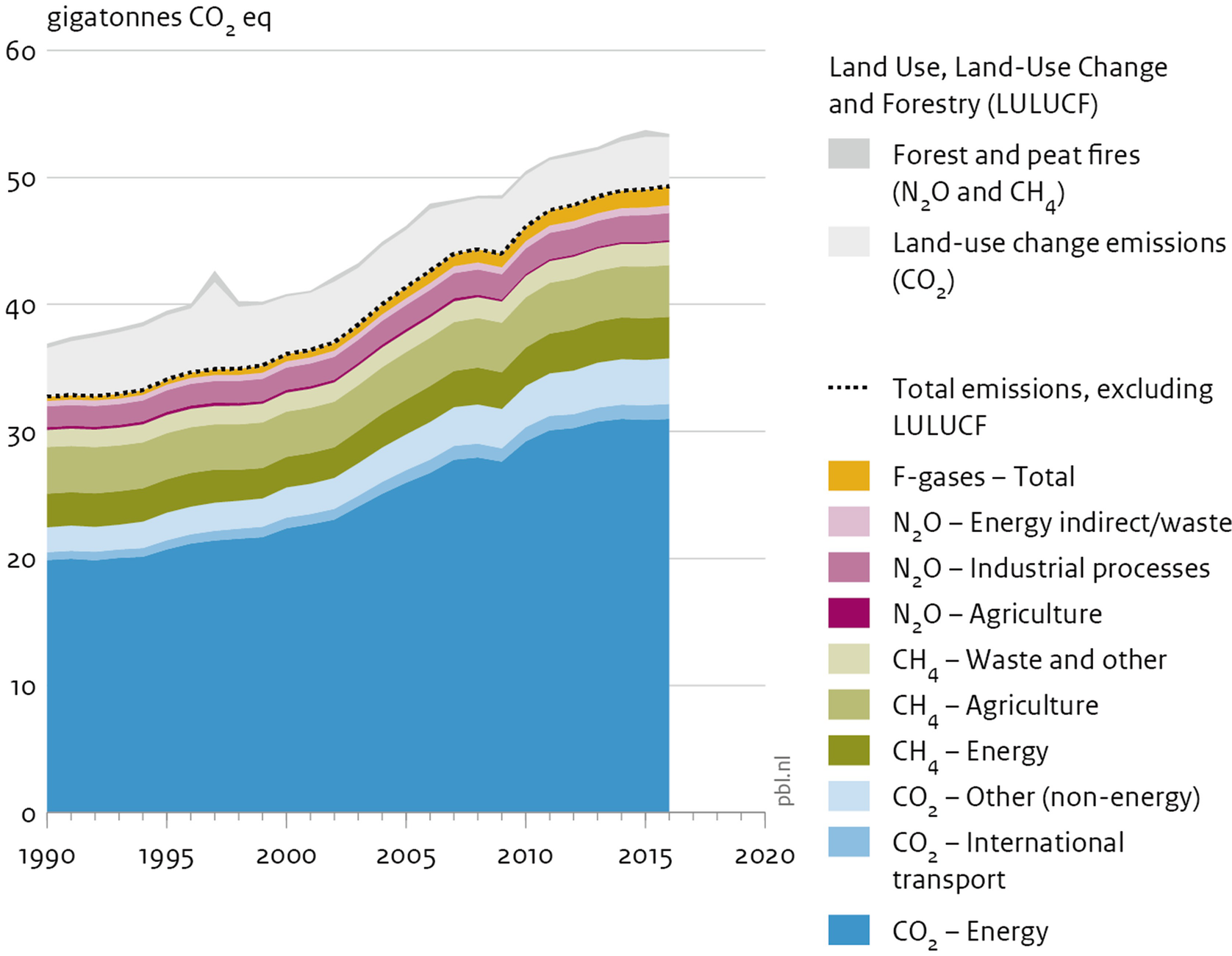



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Springerlink
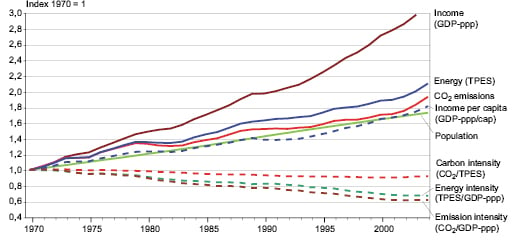



B Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends Ar4 Wgiii Summary For Policymakers



What Is A Global Warming Potential And Which One Do I Use Ghg And Carbon Accounting Auditing Management Training Greenhouse Gas Management Institute




Topic 1 Observed Changes And Their Causes Ipcc




Net Phase Out Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Newclimate Institute




New Ipcc Tier 1 Global Biomass Carbon Map For The Year 00
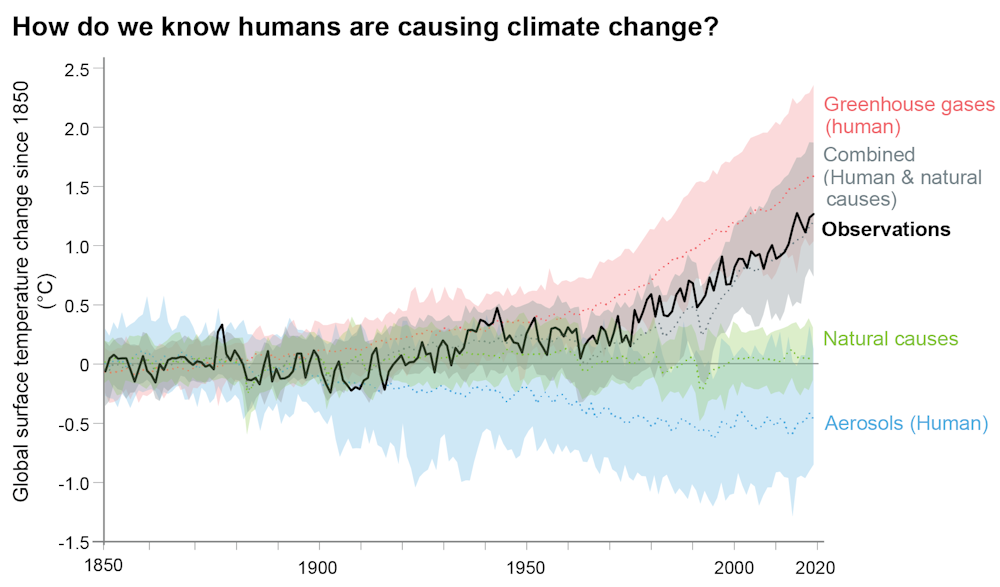



Turn Of The Tide In 1 Years Past Present And Future Of Climate



Www Unece Org Fileadmin Dam Stats Documents Ece Ces Ge 33 17 Mtg3 Session 2a 1 15h40 Ipcc Pdf
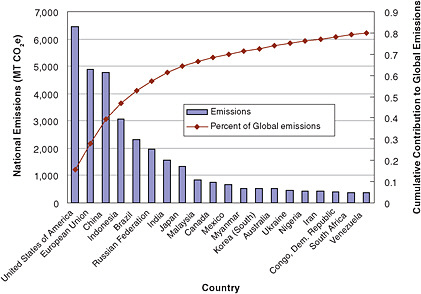



2 National Inventories Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Verifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions Methods To Support International Climate Agreements The National Academies Press
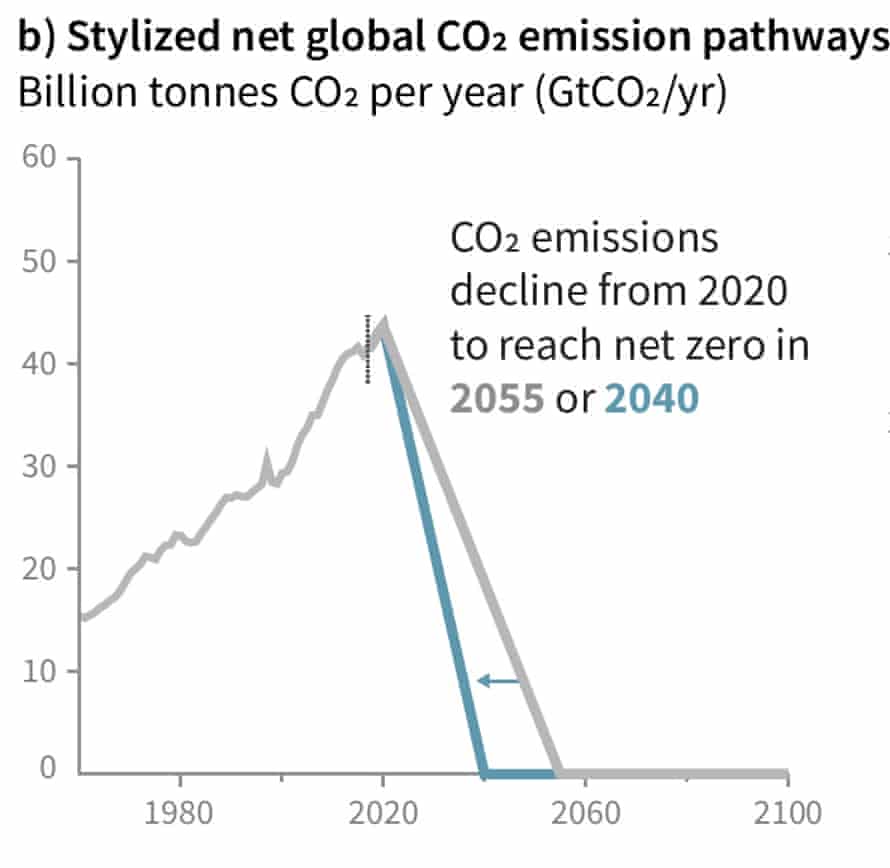



There S One Key Takeaway From Last Week S Ipcc Report Climate Change The Guardian




Radiative Forcing Atmospheric Sciences Britannica




Estimating Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Peat Combustion In Wildfires On Indonesian Peatlands And Their Uncertainty Rodriguez Vasquez 21 Global Biogeochemical Cycles Wiley Online Library



1


